
Non-Conductive Antistatic Material For ESD Protection
Opportunity
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically-charged surfaces, which can be caused by repeated contact. This is a challenge across many industries—from the oil & gas sector, where ESD can take the form of sparks and cause explosions when flammable substances are involved, to the electronics sector, where ESD is known to damage electronic components. Correspondingly, the global market for antistatic agents (compounds that eliminate static charges on a material surface) has been growing. The total market for ESD-protection products in electronic applications is expected to reach US$3.4 million in 2019 with Asia Pacific markets like China, India, Japan, South Korea, and Indonesia propping up demand.
However, the current method of addressing ESD caused by contact electrification has its drawbacks. Antistatic agents are typically applied on the surface in a coating process but this method makes it prone to wear-and-tear. Once the coating of a certain region has been worn off to the point that it becomes electrically insulated from the ground, the entire region loses its antistatic abilities.
Technology
This invention describes a homogenous and continuous material that, unlike coatings, is not prone to wear-and-tear. It is also antistatic. This is possible using an innovative method of fabrication that involves co-polymerising different proportions of two materials which are not antistatic to create an antistatic material based on a certain reference material.
The invention uses two polymers, P and N, and a reference material. While we have used a specific P, N, and reference material (glass beads) in the invention disclosure, the method is general and can be applied to many other polymers as long as one has the tendency to charge highly positive with other materials while the other has the tendency to charge highly negative. The reference material can also be changed. The resultant material is not only homogenous and continuous, it is also electrically insulated (no grounding required) and is solution-processable, which supports large-scale production.
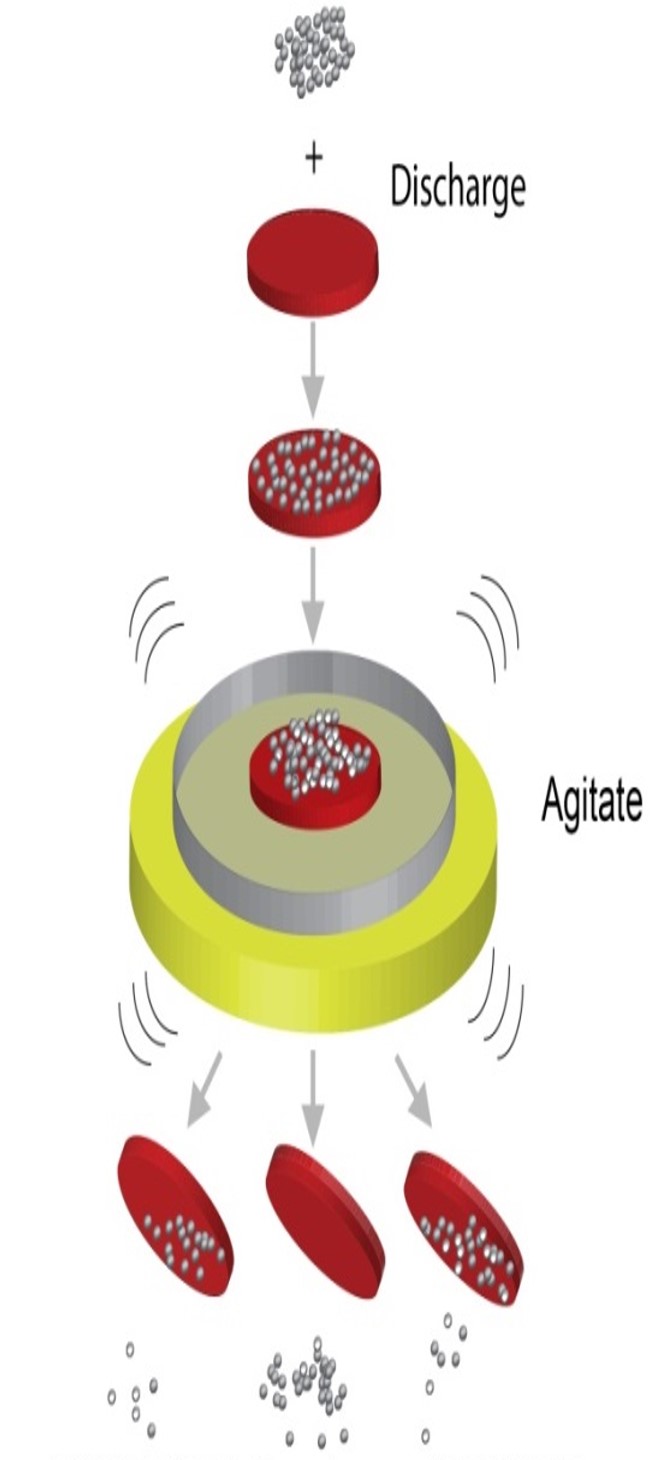
Method to optimize an anti-static polymer





