Upper Arm Wearable Device Eases Shoulder Fatigue and Prevents Injury
Opportunity
In recent years, technology developments in cloud, artificial intelligence (AI) and internet of things (IoT) have opened up new possibilities for the wearable robotic exoskeleton industry.
The compatibility of these machines to the human body structure has contributed to their wide adoption for manual labour tasks in industries such as construction, manufacturing and military. Given its potential in reducing work-related injuries, improving general work environments and elevating job standards, the market for wearable robotic exoskeletons is projected to grow from US$671.2 million in 2021 to US$8,241.7 million in 2028 at a CAGR of 43.1%.
With the aim of protecting workers from shoulder injuries and keeping resultant economic loss to a minimum, an upper arm wearable assistance device is developed to provide assist torque to the shoulder joint and relieve muscle fatigue.
Technology
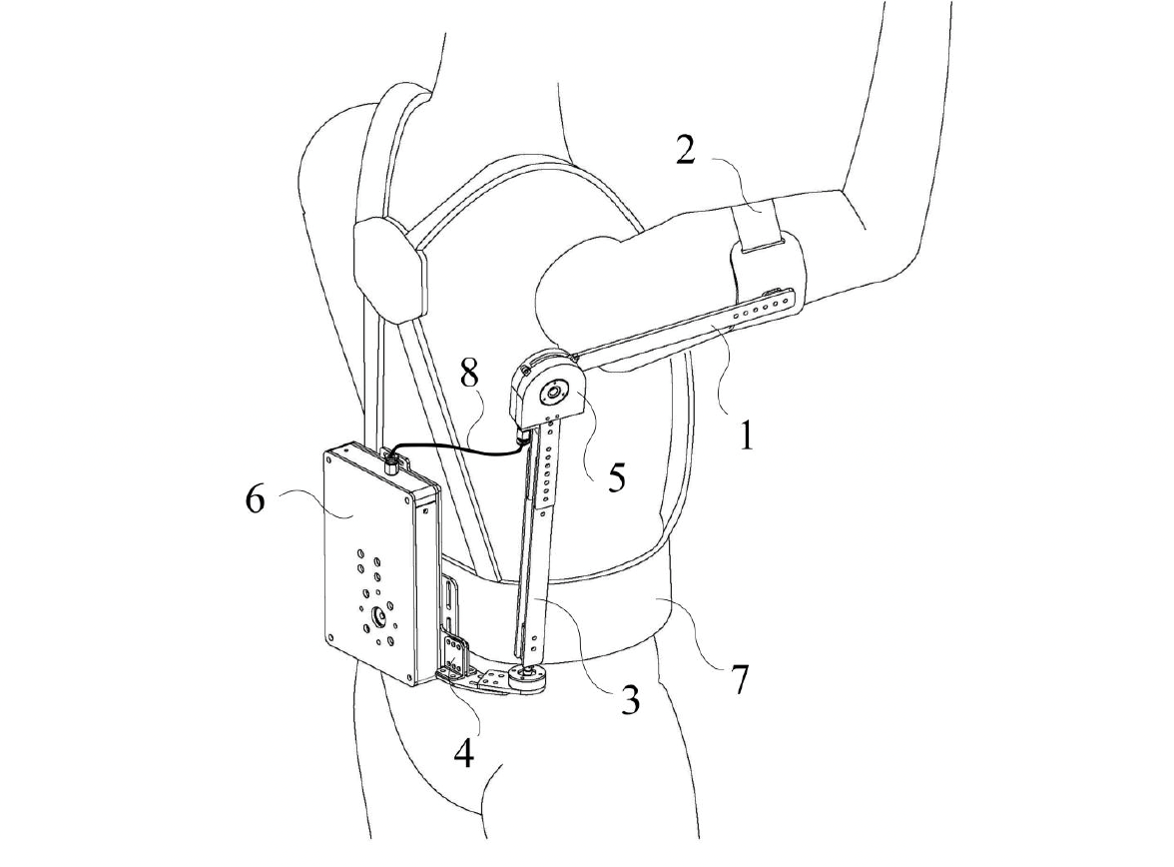
This novel wearable device provides upper arm assistance, which produces torque between upper arm and torso, to reduce muscle fatigue of the shoulder joint. The device can be used as a singular module for the left/right arm or double modules for both arms.
Each module comprises an arm link that is attached to the user’s upper arm by arm straps and a torso link fixed on a base bracket and worn on the user’s waist. A shoulder joint hinge placed parallel to the user’s shoulder joint joins the arm and torso links to allow for rotation and movement. Meanwhile, a torque generator, fixed to the base bracket, drives the pulley inside the shoulder joint hinge through Bowden cables.
In operation, the torque generator produces a resisting torque between the arm and torso links-imposing an upward pulling force on the upper arm and reducing the moment burden on the shoulder joint. The torque generator gives the largest assist torque when arm is raised perpendicular to the torso, but nearly zero torque when arm is near the natural drooping position. This ensures that the user concurrently receives support when carrying out overhead works, and no resistance when resting or performing daily activities like walking, sitting and standing.
Human Arm Assistance Device, assisting one arm in outstretching (side view).




